The TOP 5 applications of LiDAR solutions
From smart cars and robots to logistics, construction, and agriculture, multiple businesses are impacted today by LiDAR's flexible and highly precise solutions
Let’s start with a brief introduction: LiDAR technology is a type of optical technology that uses infrared light to measure distances, localize an object, or create a map of an area. It is one of the most useful and versatile technologies of our time.
It could be used in almost any industry, from smart cars and robots to logistics, construction, forestry, and agriculture. In this guide, we'll deep-dive into the top five most relevant applications of LiDAR technology. If you want a good overview of how LiDAR is mostly being used, you will enjoy this article.
ADAS
When most people think of the top applications of LiDAR, they think of autonomous cars, but LiDAR has a much wider role to play in the automotive industry, especially with ADAS, or advanced driver assistance systems, which are designed to avoid collisions and create safer situations for road users. Unlike traditional safety measures like the seat belt (passive), ADAS are active safety solutions.
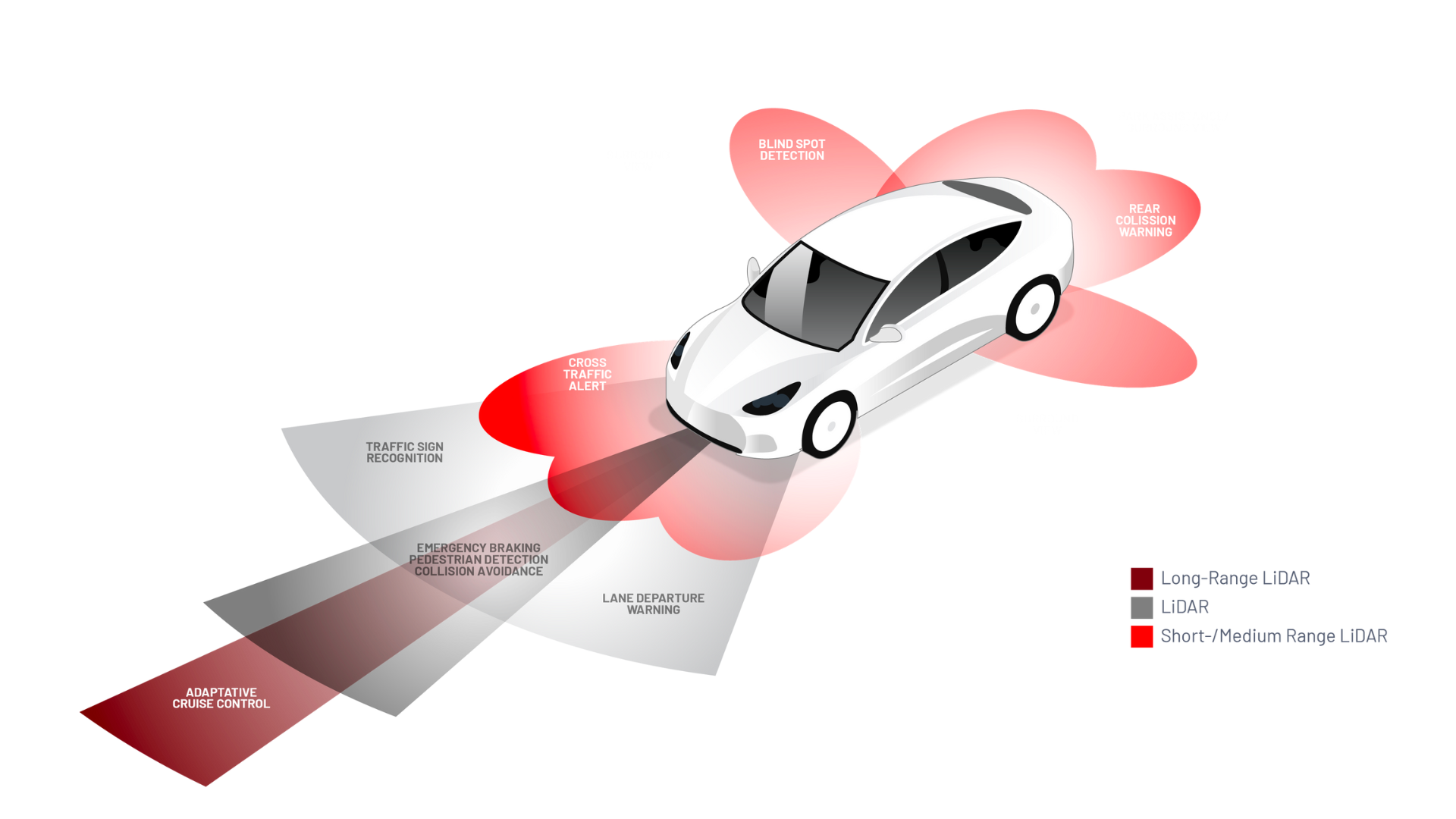
Examples of LiDAR technology being used for ADAS include lane departure warnings, blind spot detection, and adaptive cruise control.
These modern automotive features may be built directly into vehicles or offered as aftermarket solutions.
Today, according to Canalys research1, an increasing number of vehicles are manufactured with ADAS features built-in: the percentage of cars in use with ADAS feature shall go from 10% in 2020 to 30% in 2030 and 50% in 2050 . These safety measures are required to get the desired results on new vehicle assessment ratings such as EuroNCAP.
Use Case: Commercial Vehicles Safety
A growing number of commercial vehicles, such as trucks, are incorporating LiDAR hardware.
For reference, the global autonomous truck market was valued at USD 846.2 million in 2019 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 12.8% through 2027, according to Polaris Market Research2.
As one of the most dangerous industries, the world of trucking can massively benefit from LiDAR technology to improve driver safety, as well as reducing the risk of accidents in locations like construction sites and mines.
Indeed, LiDAR can play a decisive role to anticipate dangerous situations. It can provide essential data to detect, for example, an obstacle or reveal the presence of pedestrians or bicyclists. In these cases, the vehicle can activate the appropriate emergency systems such as automatic braking or lane keeping assistance.
Use Case: Self-Driving Cars
It is becoming more evident that LiDAR sensors will be necessary for Level 4 (High Driving Automation) and Level 5 (Full Driving Automation) autonomous vehicles. As an example, the car manufacturer Mercedes has already planned to integrate it into its top-of-the-range models to assist autonomous driving in its production vehicles.
One reason why LiDAR technology is so important for self-driving cars is that it helps make sure that, even in unknown environments, cars follow the correct route and pose no unnecessary risks to passengers or other road users.
As an example, Outsight supported the creation of fully autonomous shuttle to navigate through a university campus using Outsight’s LiDAR software. The shuttle is capable of detecting moving objects and adjusting its route to avoid them.
Use Case: Generating Reference Data
At this time, LiDAR sensors are being used to generate useful reference data that can be harnessed to benchmark the performance of other kinds of sensor technology, like radars and cameras on moving vehicles.
Therefore, this data can be used to make other technologies even more efficient when it comes to providing safe road conditions for users.
By creating Ground Truth data with Outsight software, it is possible to have a reliable source of tracked objects, both dynamic and static (landmarks).
Smart Infrastructure
Smart Cities and related topics, such as Intelligent Transportation Systems, or ITS, are becoming increasingly popular around the world, and it's clear that LiDAR technology will play a key role in the growth and development of Smart Cities.
The main reasons are that LiDAR's 3D data is very precise and operates in a variety of settings, including direct sunlight and at night, unlike 2D perception systems like cameras. Besides, LiDAR technology also addresses privacy in Smart Cities, as it never collects personal data.
In fact, the worldwide smart city market is expected to reach US$2.86 trillion in 2026, growing at a CAGR superior to 20% between 2022 and 20263, fuelled by increased global urbanization and rising technology spending on smart city efforts.

There’s lots of scope for this technology to be used further in Smart Cities, and there are already plenty of examples of LiDAR applications for smart infrastructure, including:
Use Case: Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS)
One of the main applications of LiDAR is ITS. In this case, Outsight’s Augmented LiDAR software can be used, along with LiDAR sensors, to detect and track both vehicles, pedestrians, and other objects in a large surveillance area. The LiDAR system can then be fine-tuned for different applications such as crosswalk safety, over-speed alerts, pedestrian near-misses, and more.

The output is an actionable Dashboard with both real-time alarms triggered by specific events or aggregated data over long periods of time.
Use Case: Anonymous People Tracking
In many ways, airports are like small, enclosed cities of their own, complete with paths, walkways, flows of people, parkings, retail zones, and more.
By combining Edge AI and cloud-based technology, the Augmented LiDAR software carries out enhanced spatio-temporal visual analysis of large spaces like train stations, malls, airports, and more. This allows for precise detection, tracking, and understanding of crowds of people anonymously.
Unlike Camera Face ID, LiDAR data allows for exact detection and tracking of persons and objects, but the resolution of even the best-performing sensors does not allow for recognition, rendering this technology completely anonymous.
Additionally, LiDAR solutions can effective in luggage tracking and preventing los luggage which are likely to cause significant delay.
These functions also apply for train stations, subway, and other modes of public transportation.
Use Case: Spatial Intelligence and Security
Another one of the top applications of LiDAR is for Spatial Business Intelligence.
LiDAR sensors can be used to track and generate actionable metrics about a range of actions and situations throughout an airport environment, including customs and passenger flows through security and other key areas, luggage belt optimization, seat occupancy, and more.
It can also be used for security purposes, generating alerts instantly about unexpected events if some metric reaches a threshold or if a security zone or perimeter is invaded.
Robotics
Another one of the top five applications of LiDAR is in regard to robotics.
This industry is growing larger and more significant with every passing year, and the rate of development shows no signs of slowing down, with a global growth rate of 15.3% according to Renub Research4.
For those wondering, LiDAR technology is at the core of the smart vehicle and robotics revolutions.

The main application of LiDAR in terms of robots is to make them safer to work with and be around. Due to the autonomous nature of their operations, these machines require the highest standards of safety technology, and LiDAR sensors can be used to reduce the risks of accidents or injuries involving them.
Use Case: Path Following for Deliveries
Let's imagine that you have an automated guided vehicle, or AGV, inside a warehouse. The vehicle needs to be able to navigate safely and accurately to specific pick-up and delivery locations in the warehouse environment.
LiDAR-enabled path following with Outsight’s relocalization technology can allow the robot to understand not only how it’s moving but also where it is in a reference map - for example, a warehouse map.
Use Case: Security Robots
One of the main ways in which robotics and 3D LiDAR can work together is in the form of security robots. These robots may be instructed to move around areas of interest, like the perimeter of a building, following a set trajectory. An operator may wish to re-localize the robot's route after an event, which is where the 3D LiDAR comes into play.
Use Case: Fleets
3D LiDAR can also be of great use in situations involving multiple smart robots or vehicles operating as part of a unit or fleet and sharing the same space. The vehicles or robots need to be aware of their respective positions and orientations in order to operate safely together. Once more, LiDAR technology can assist in this scenario.
Industrial
Arguably one of the most widespread of the top applications of LiDAR technology is in the world of industrial safety; LiDAR hardware and software can be used to improve safety in industrial workspaces, as well as raising the levels of productivity and efficiency for businesses with the aid of real-time 3D insights.

With its reliable data and adaptable nature, LiDAR technology can be used in industrial markets to make many situations and places safer for workers to operate.
According to a report done by The Insight Partners, the industrial automation market is expected to reach 238 billion dollars in 2028, with an average annual growth rate over 7%5.
Use Case: Construction Site Safety
Construction sites can be some of the most dangerous places. A great application for 3D LiDAR is to help improve safety standards in and around these areas. LiDAR software can be used to track distances between human workers, large machines, vehicles, and so on, and alerts can be issued if dangerous situations arise.

Use Case: Teleoperation of Heavy Equipment
One of the most interesting growing trends in terms of applications and uses of LiDAR is to provide pathways for third-person teleoperation of heavy items of equipment and machinery in industries like mining and construction.
3D LiDAR, when equipped with the right software, provides the unique capability for remote operation in a 3rd person point of view, in real-time, providing high levels of accuracy and reducing accident rates when working with heavy machines.
Use Case: Volume Measurement
Another industrial application of 3D LiDAR is to determine the volume of objects, like trucks for instance, as they pass through a gantry.
In this example, an augmented LiDAR software can allow users to leverage LiDAR technology to autonomously detect load volume of each vehicle, saving huge amounts of time and simplifying a formerly complex process.
Mapping
Finally, the last of the top five applications of LiDAR is mapping.
LiDAR mapping is probably the oldest application of LiDAR, although still a rapidly-growing field of technology, and it's possible to look at thousands of potential and current use cases when it comes to using 3D LiDAR for mapping in industries like forestry, agriculture, city planning, and so on.

LiDAR mapping involves the use of laser scanning systems and advanced SLAM algorithms to precisely measure and map out a space with accurate georeferencing, forming a precise 3D representation of the target area.
LiDAR maps are unique in that they provide absolute positional accuracy, and it's possible to map entire cities in this way. Here are some example use cases:
Use Case: High-Density 3D Mapping
Thanks to the high-grade technology of modern ALB devices, it's possible to make high-density 3D maps in no time at all.
Entire cities or sections of land can be mapped in 3D with stunning levels of precision, and these maps can be used by anyone from city planners to forestry companies. For reference, one of Outsight clients used our software’s mapping feature to localize all street lamps from a certain region in a map.
Use Case: Forestry Management
Following on from the previous point, the forestry industry is one that can greatly benefit from the applications of LiDAR technology.
LiDAR can make 3D maps of forests, which can be crucial when it comes to forest management and development over time. In practice, thanks to Outsight’s software, a ground operator can easily create a forest map.
Use Case: Trains

Another use of LiDAR mapping is for railways and trains. Long-range and medium-range LiDAR detection devices can be used to map out the spaces around railway tracks, and it's even possible to carry out vegetation monitoring along rail routes. All of this can be utilized to make trains safer, smarter, and more efficient.
LiDAR: Technology with Endless Application Potential
Thanks to LiDAR software, now 3D LiDAR can be applied to almost endless use cases.
From making industrial environments safer to helping with forest management and paving the way for the future of safe, autonomous cars, there are no limits to what can be accomplished with this technology.
Almost anything that moves or requires some sort of movement monitoring or measurement can be improved and optimized with the aid of 3D LiDAR.
At Outsight, we're making use of real-time software to push the limits of LiDAR even further.
Contact a product specialist today to learn more or download our most recent whitepaper about one of the applications overseen in this article:

Sources
- canalys.com, “Huge opportunity as only 10% of the 1 billion cars in use have ADAS features”, Sep 2021
- polarismarketresearch.com, “Autonomous Truck Market Share, Size, Trends, Industry Analysis Report By Level of Autonomy (Level 1, Level 2, Level 3, Level 4, Level 5); By Sensor Type (Radar, LiDAR, Camera, Ultrasonic); By End-Use (Logistics, Construction & Manufacturing, Mining, Port); By Region - Segment Forecast, 2020 - 2027”, Aug 2020
- ResearchAndMarkets.com, “Global Smart City Market (By Application & Region): Insights & Forecast with Potential Impact of COVID-19 (2022-2026)”, May 2022
- globalnewswire.com, “Global Robotics Market is projected to grow to US$ 86.20 Billion by 2027”, Nov 2022
- theinsightpartners.com, “Industrial Automation Market Forecast to 2028 - COVID-19 Impact and Global Analysis By Component (Hardware and Software), System Type (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition, Distributed Control System, Programmable Logic Control, and Others), and End Users (Oil & Gas, Automotive, Food & Beverage, Chemical & Materials, Aerospace & Defense, and Others)”, Mar 2022